The Product Carbon Footprint (PCF)
A PCF measures the sum of GHG emissions generated during the life cycle of a product. This enables to focus on the most significant emission sources. E.g., we can optimize logistical routes or replace purchased parts by less carbon intensive ones. With customers also investigating their supply chain, to deliver and improve PCFs becomes increasingly business critical.
A PCF is a type of Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). Where a life cycle assessment can focus on many types of environmental impacts (e.g. water use, eutrophication, land use change etc.) a PCF only focusses on one type of impact: Greenhouse Warming Potential or CO 2e emissions. A PCF is different from a Corporate Carbon Footprint (CCF). A PCF considers product level and often emissions that are not directly related to the production (such as commuting to work) are excluded. While the CCF calculates the total direct emissions (Scope 1 &2) and indirect (Scope3) generated by all activities at company level.
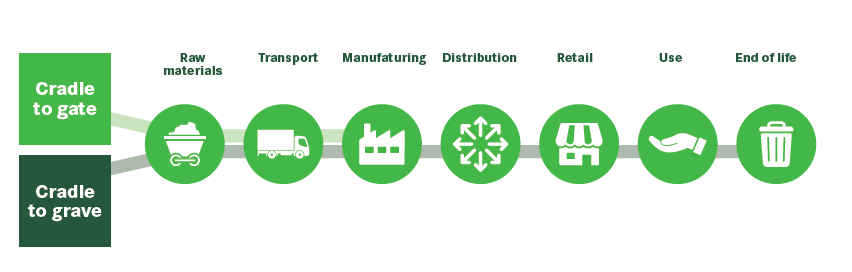
Cradle to Gate & Cradle to Grave
PCFs can be calculated via a Cradle to Grave- or a Cradle to Gate-approach. Cradle to Grave considers GHG emissions starting from extraction of raw materials until end of life of the product. A Cradle to Gate-approach finishes at the exit gate of the factory. The Cradle to Gate-approach is most used for Business to Business (B2B)-type of companies as it avoids double counting of emissions.
When suppliers are not able to provide PCFs yet, an environmental database with standard values for products and processes can be used to fill data gaps. HARTING works with EcoInvent, a well-known life cycle inventory database when no data is available from suppliers.
PCF@HARTING
At HARTING we consider the PCFs as complementary perspective in addition to the CCF. Since our products are used in different applications, we focus on the Cradle to Gate PCF. Developing a PCF case by case is costly and time intensive and does not suit the rapid developments. In August we have kicked off a pilot project to calculate PCFs in a more automated way. As a proof of concept, we will set up a PCFs calculation process and tool and validate its applicability by calculating 100 articles from our iconic Han® connector range using SAP SFM. The result of the PCF we can then share as a product digital twin through the Asset Administration Shell and the digital product pass. HARTING expects to benefit from integration with our current SAP S4H production environment, where data is stored that is needed to calculate footprints.
IoT
The PCF-pilot project is one of the first projects to make use of the directly measured energy data from our highly automated manufacturing plant in Espelkamp..
Outlook
PCF is a quickly developing field, where currently many companies are still developing competences and methods to be able to provide data on their PCF performance. We also believe this should be the priority now. Throughout the following months and years, we expect to see many developments:
- Delivering (automated) data on PCF of our products
- Improving data quality by increasing the share of directly measured data
- Working together with sector partners towards further standardization to increase the
comparability (HARTING works with VDMA & ZVEI) - Using PCF in the product development and work together with customers and suppliers on
data sharing and improvements to reduce carbon intensity in our supply chains. - Shift from a product carbon footprint to a “service carbon footprint”, based on the carbon
intensity of the performance rather than the product
At HARTING we believe we can work together with customers and suppliers to reduce the emissions in the supply chain through the Product Carbon Footprint.